The integration of automotive part is like assembling building blocks, connecting circuits, and adding energy drinks. Various components are precisely assembled on an assembly line, ultimately becoming a mobile steel partner.
Content
- 1 I. Underlying Skeleton: Body Frame (Car Skeleton)
- 2 II. Powertrain Integration: Engine + Transmission (Heart + Stomach)
- 3 III. Chassis System Mounting: Chassis Components (Legs and Feet)
- 4 IV. Nervous System Wiring: Circuits + Sensors (Brain Nerves)
- 5 V. Breathing and Circulation System: Fluid Lines (Car Blood Vessels)
- 6 VI. Exterior Packaging: Interior and exterior trim (like a coat)
- 7 VII. Vehicle Tuning: Final Break-in (Character Development)
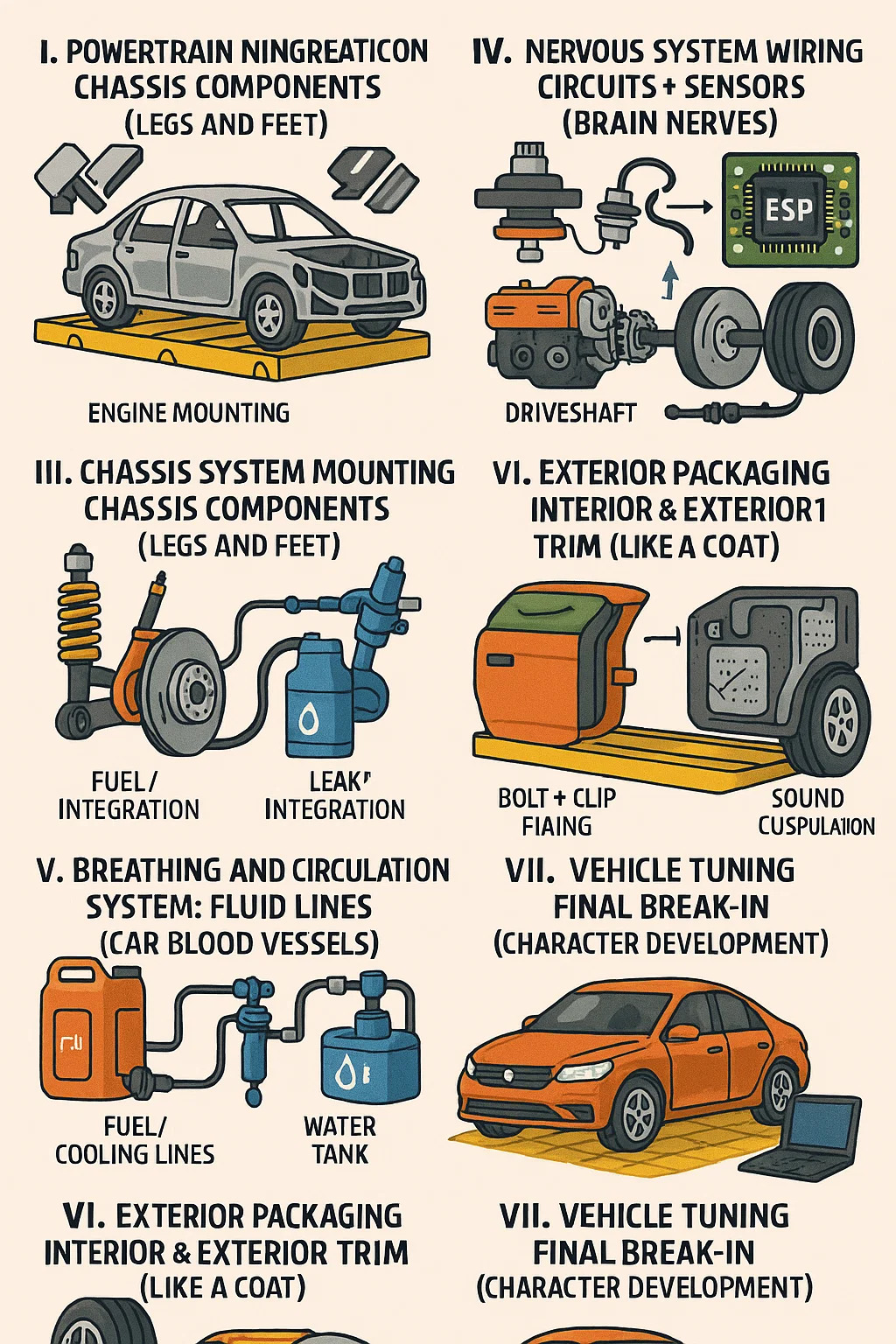
I. Underlying Skeleton: Body Frame (Car Skeleton)
Stamping and Welding: Steel plates are pressed into shapes such as doors and roofs, and assembled into a cage-like skeleton using over 3000 weld points for protection in collisions.
Using Different Strength Steels: The A-pillar uses hot-formed steel (the hardest), while the rear trunk uses soft steel (energy-absorbing), like the balance of strength and flexibility in Tai Chi.
II. Powertrain Integration: Engine + Transmission (Heart + Stomach)
Engine Mounting: The engine is fixed to the frame with rubber mounts to absorb vibrations; otherwise, the steering wheel would vibrate like a massager.
Driveshaft Connection: The transmission output shaft is inserted into the driveshaft universal joint to transmit power to the rear wheels (rear-wheel drive) or front wheels (front-wheel drive).
III. Chassis System Mounting: Chassis Components (Legs and Feet)
Suspension Assembly: The upper end of the shock absorber is screwed onto the frame, and the lower end connects to the control arm, which in turn connects to the wheel hub—forming a "wheel seesaw" to filter bumps.
Brake Integration: The brake caliper acts like pliers, clamping the brake disc. The fuel line connects to the brake pedal in the driver's cabin; pressing the pedal is like squeezing the pliers to slow down.
IV. Nervous System Wiring: Circuits + Sensors (Brain Nerves)
Wiring Harness Assembly: Bundling wires into a main line (like a tree trunk), branching out into smaller harnesses to connect to headlights and audio systems (like tree branches). The entire wiring harness, when stretched out, could circle a football field three times.
Sensor Interconnection: Wheel speed sensors detect slippage → the signal is transmitted to the computer → the ESP system applies the brakes to revive the vehicle, reacting 10 times faster than the human brain.
V. Breathing and Circulation System: Fluid Lines (Car Blood Vessels)
Fuel/Cooling Lines: The fuel tank → fuel pump → fuel injectors form a "fuel supply channel," while the water tank → water pump → engine block form a "cooling tea."
Leak-proof sealing: Rubber hoses are secured to metal connections with clamps; leaks of oil or coolant will render the vehicle unusable.
VI. Exterior Packaging: Interior and exterior trim (like a coat)
Bolt + Clip Fixing: The front bumper is secured to the frame with 8 bolts; interior panels have concealed plastic clips—they'll break if you try to force them.
Acoustic Encapsulation: Sound insulation cotton is applied to the firewall, and recycled cotton is stuffed into the door panels; otherwise, the engine noise will be like a concert right next to your ear.
VII. Vehicle Tuning: Final Break-in (Character Development)
Four-Wheel Alignment: Adjusting the toe angle ensures the car travels in a straight line; adjusting the camber angle prevents uneven tire wear.
ECU Calibration: Engineers reprogram the system to determine throttle response, allowing even small-displacement cars to respond precisely to the pedals.

 English
English Español
Español

