Die casting machinery parts are the "bones" and "joints" of industrial equipment, manufactured through metal high-pressure forming technology to solve complex structural, strength, and efficiency requirements that traditional processing cannot achieve. The following are its core application areas:
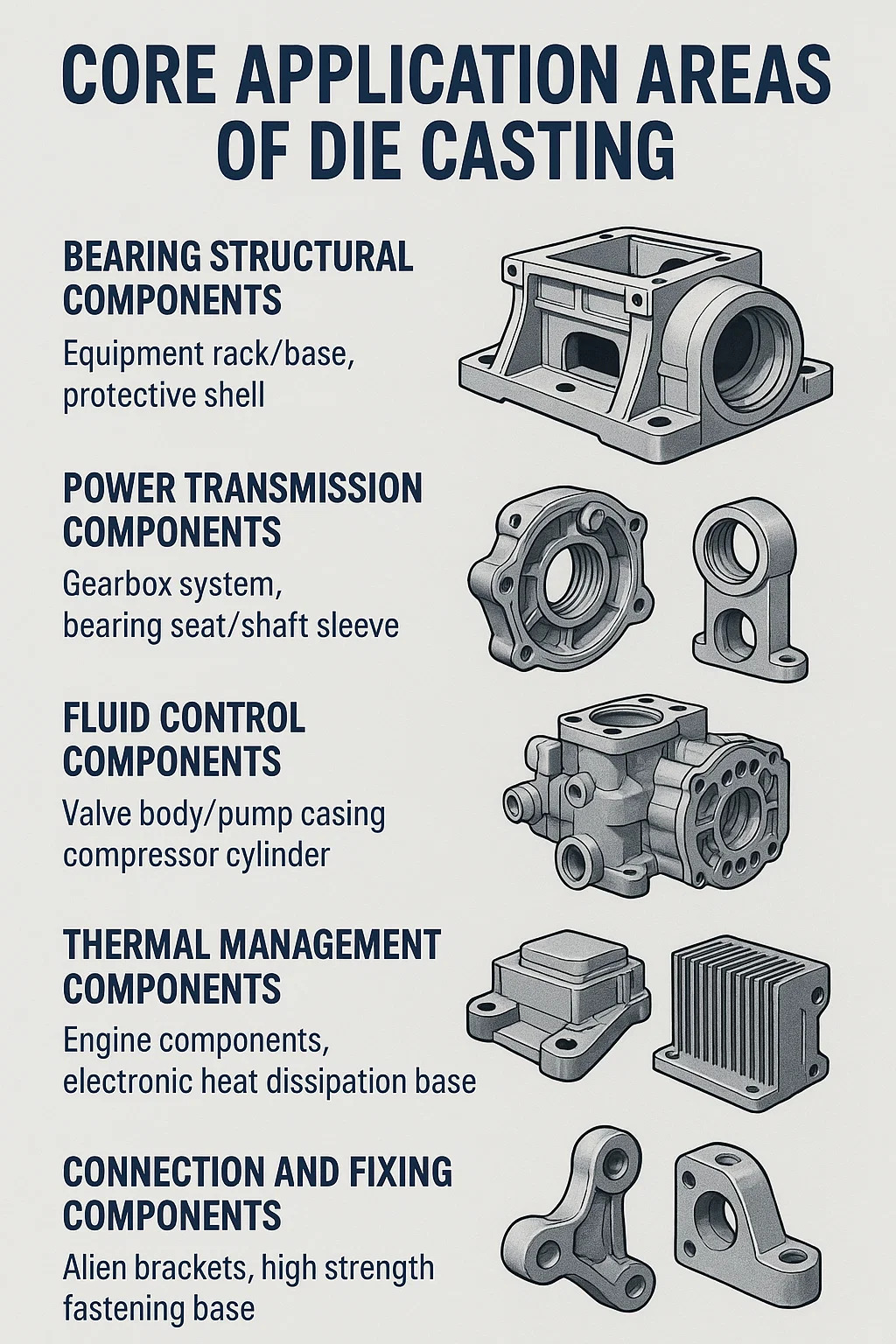
1. Bearing structural components - the foundation skeleton of the equipment
Equipment rack/base: such as CNC machine tool base, injection molding machine template, can withstand the weight and vibration of the whole machine, and die castings are designed with reinforcing ribs to achieve lightweight and high rigidity.
Protective shell: Industrial robot protective cover, motor shell, providing impact protection while isolating dust/liquid intrusion.
2. Power transmission components - media for energy conversion
Gearbox system: electric tool reduction gear, car wiper worm gear, utilizing the high wear resistance of zinc alloy to transmit torque.
Bearing seat/shaft sleeve: Accurately fix bearings in high-speed rotating equipment (such as water pumps and fans) to reduce friction and vibration.
3. Fluid control components - checkpoints for sealing and flow guidance
Valve body/pump casing: Hydraulic directional valve block, fuel pump casing, relying on die cast internal flow channels to achieve directional liquid/gas delivery, replacing multi piece welding assembly.
Compressor cylinder: The air conditioning compressor accommodates piston movement and requires high pressure resistance and dimensional stability (aluminum alloy die-casting+precision machining).
4. Thermal management components - the "movers" of heat
Engine components: internal combustion engine cylinder head cover, turbocharger housing, utilizing the rapid thermal conductivity of aluminum alloy to disperse high temperatures.
Electronic heat dissipation base: frequency converter heat dissipation module, LED drive power supply housing, passive heat dissipation through fin structure.
5. Connection and fixing components - the "adhesive" of the equipment
Alien brackets: automotive sensor brackets, aviation equipment lifting ears, suitable for irregular installation spaces.
High strength fastening base: installation base for hydraulic blocks in construction machinery to avoid hole displacement caused by welding deformation.
Why is it necessary to die cast? Key irreplaceability
Complex structure integrated molding: such as brake caliper housing with internal oil channels, which cannot be machined.
Cost advantage of 10000 pieces: The unit price of gearbox die-casting parts is only 1/5 of CNC machining (during mass production).
Maximizing material performance: The strength of die cast aluminum alloy is more than 20% higher than that of sand castings of the same material.
Typical Industry Application Scenarios
| Industry Sector | Key Die-Cast Components | Critical Value Proposition |
| Automotive | Transmission valve bodies, engine brackets, sensor housings | Lightweighting for housings |
| Industrial Machinery | Robotic arm joints, CNC machine frames, pump impellers | High stiffness-to-weight ratio; precise tolerances for motion control |
| Aerospace & Defense | Drone motor mounts, avionics enclosures, weapon system triggers | Extreme weight reduction system triggers |
| Consumer Electronics | Power tool gearboxes, camera lens barrels, laptop heat spreaders | Complex internal geometries; thermal management in compact spaces |
| Energy Infrastructure | Solar inverter casings, hydraulic valve blocks, wind turbine controllers | Corrosion resistance for outdoor exposure; sealing against dust/moisture |
| Medical Equipment | Imaging device rotors, surgical tool handles, ventilator manifolds | surgical tool handles, ventilator manifolds |

 English
English Español
Español

